Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs): Pillars of a Strong Financial Ecosystem
Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs): Pillars of a Strong Financial Ecosystem
Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs) are the backbone of a robust and well-regulated financial market. These institutions include stock exchanges and depositories that facilitate seamless trading, clearing, and settlement of securities, ensuring transparency, investor protection, and financial stability. Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates MIIs to maintain transparency, investor protection, and financial stability i.e. the integrity of the financial ecosystem.
Why are MIIs Important?
MIIs ensure that financial transactions are executed efficiently and securely. Their role is critical in maintaining investor confidence, reducing systemic risk and enabling smooth capital market operations.
Part I: Stock Exchanges – Driving Capital Market Efficiency
What are Stock Exchanges?
Stock exchanges provide a centralized platform where investors can buy and sell financial instruments like stocks, bonds, and derivatives. They ensure fair and efficient price discovery, liquidity and transparency thereby contributing to the overall stability of financial markets.
Roles of Stock Exchanges
Trading Platform: Exchanges provide a structured and regulated environment where buyers and sellers can trade securities efficiently.
Liquidity: Exchanges allow investors to buy and sell securities, ensuring that the investors can exit or enter positions easily.
Price Discovery: Through continuous trading, exchanges help in determination of the fair valuation of securities based on demand and supply.
Regulatory Oversight: Exchanges monitor trading activities and follow SEBI regulations to prevent fraud, insider trading and market manipulation.
Economic Growth Enabler: Companies raise capital through stock exchanges by issuing shares, contributing to economic expansion

Key Stock Exchanges in India
National Stock Exchange (NSE)
- Established in 1992, NSE is the largest stock exchange in India in terms of trading volume.
- NSE’s benchmark index, NIFTY 50, is a crucial indicator of market trends.
- NSE introduced fully electronic trading ensuring speed, transparency and efficiency
- NSE is the major platform for derivatives trading in India
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
- Specializes in commodities trading, such as gold, crude oil, and metals
- BSE’s benchmark index SENSEX, is a crucial market indicator that represents India's top 30 companies.
- Offers a wide range of financial products, including equities and mutual funds.
- BSE provides a robust platform for equity, debt, and derivative trading.
Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX)
- Specializes in commodities trading, such as gold, crude oil, and metals.
- Helps businesses and investors to hedge against price fluctuations.
National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange (NCDEX)
- A key exchange that facilitates agricultural commodity trading such as wheat, barley, chana bajra, soybean etc.
- Aids in stabilizing farmer incomes and managing risks in the agricultural sector.
Metropolitan Stock Exchange of India (MSEI)
- A relatively newer exchange focusing on equity, debt, and currency markets


How Exchanges Benefit Investors:
Transparency: Ensures fair pricing through electronic trading.
Security: Regulated by SEBI to protect investor interests and prevent market manipulation.
Diverse Investment Opportunities: Investors can access a variety of products like equities, derivatives, commodities, and currency segments.
Global Recognition: Indian stock exchanges are among the largest in the world.
PART II: DEPOSITORIES – Securing Investor Assets
What are Depositories?
Depositories provide a secure and paperless way of holding securities electronically. They eliminate the need for physical certificates, reducing risks such as theft, loss, or forgery. They play an essential role in the overall functioning of the financial system by ensuring:
Roles of Depositories
Electronic Custody: Investors' securities are held in a digital format, reducing risks of loss or forgery.
Efficient Settlement: Depositories ensure timely and accurate transfer of securities after a trade.
Corporate Actions Management: They help in the seamless processing of dividends, interest payments, stock splits, and bonus issues in the demat account of the investors
Pledging & Borrowing: Investors can pledge securities as collateral for loans without requiring physical certificates.
Regulatory Compliance: Depositories maintain record of ownership and transactions, ensuring market transparency and accountability.
Key Depositories in India
National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL)
- Established in August 1996, NSDL introduced dematerialization in India.
- Facilitates seamless transfer of securities between investors and exchanges.
- Offers services such as e-Voting and electronic verification of securities
Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL)
- Established in February 1999, CDSL provides electronic holding and settlement services.
- Simplifies corporate actions like dividends, rights issues, and bonus shares.
- Offers a simplified account opening process for investors.
How Depositories Benefit Investors
Secure Holding: Eliminates risks of physical theft, loss of documents and forgery of physical certificates.
Convenience: Enables smooth buying, selling, and pledging of securities.
Cost-Effective: Investors can access their holdings online anytime, ensuring transparency and ease of use.
Enhanced Accessibility: Investors can access their holdings online anytime, ensuring transparency and ease of use.
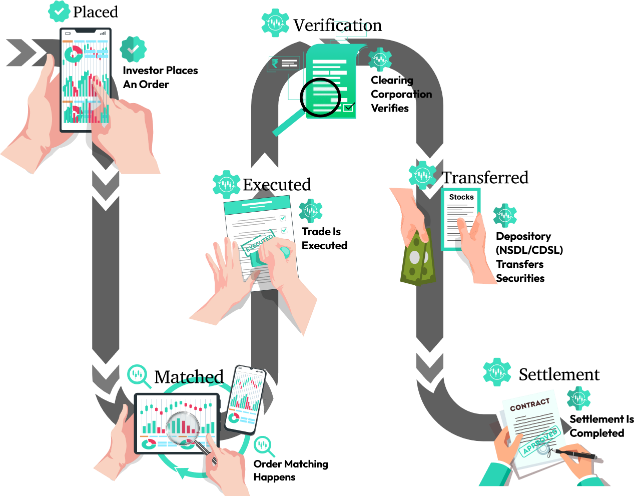
How a Trade Works in the Indian Financial Market:
Investor places an order on NSE/BSE through a broker.
Order matching happens based on price and volume.
Trade is executed and recorded by the exchange.
Clearing corporation verifies funds and securities availability.
Depository (NSDL/CDSL) transfers securities from seller to buyer.
Settlement is completed and reflected in investors' demat accounts